HVAC Energy Consumption in North America: An Analysis of the Industry's Energy Footprint
- Ava Montini
- Sep 16, 2024
- 7 min read
Picture walking into an office on a hot summer day, where the air is refreshingly cool, or entering a cozy, warm home on a chilly winter evening—have you ever wondered how much energy it takes to maintain that comfort year-round?
This climate-controlled comfort is brought to you by HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, which are indispensable for indoor environments. However, this convenience comes at a substantial cost: HVAC systems are among the largest consumers of energy in North America. HVAC operations represent a considerable portion of total energy consumption, making them central to discussions about sustainability and environmental impact.
Understanding the scope of this energy use and the underlying factors is key to addressing one of the most critical challenges facing the energy sector today.
HVAC Energy Consumption: The Scope of the Problem
In North America, HVAC systems are a significant contributor to energy consumption. According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), HVAC systems account for around 40% of the energy used in commercial and residential buildings, which places a substantial burden on energy resources. HVAC systems account for approximately 35% of total energy consumption in U.S. commercial buildings, and around 45% in residential buildings, primarily due to heating, cooling, and ventilation demands. In Canada, this figure tends to be higher because of more extreme temperature variations, particularly during the winter months (EIA Energy).
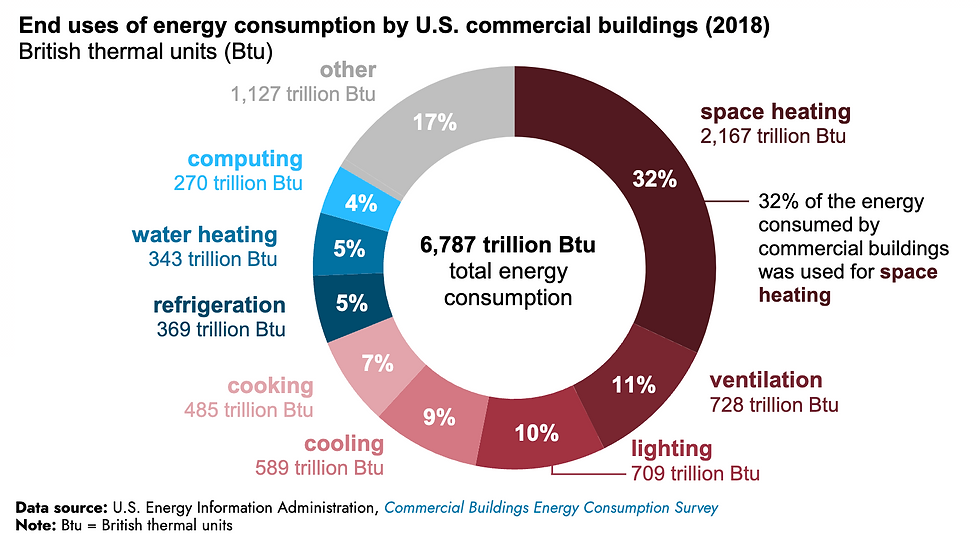

This energy consumption not only leads to escalating operational costs but also exacerbates carbon emissions. Most of the energy powering HVAC systems is derived from fossil fuels, creating a double-edged sword: while these systems make indoor spaces more livable, they also significantly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. If HVAC energy usage continues on this trajectory, it will hinder efforts to meet global climate targets.
Why Is HVAC Energy Consumption So High?

1. Aging Infrastructure
A substantial portion of North America’s building stock is decades old, and many of these structures have outdated HVAC systems. These legacy systems were designed at a time when energy efficiency standards were far less rigorous, leading to inefficient heating, cooling, and ventilation.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), HVAC systems in buildings older than 20 years use 20-30% more energy to operate than those in modern buildings equipped with energy-efficient systems. The cost of replacing or retrofitting these systems can seem prohibitive, leading to a cycle of inefficiency as property owners defer necessary upgrades.

2. Slow Pace of Innovation
Despite significant advancements in other areas of building technology, the HVAC industry has been slow to adopt cutting-edge innovations. Technologies like smart HVAC systems, smart thermostats, and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) can significantly reduce energy consumption, but their adoption has been sluggish. Many commercial and residential properties still operate with older systems that don’t leverage real-time data or optimize energy usage based on demand.
The lack of integration between HVAC systems and broader building management systems further limits opportunities for energy savings. This stagnation in the industry has left buildings operating at inefficient levels, unable to keep up with modern sustainability standards.

3. Climate and Seasonal Extremes
The geographic diversity of North America means that HVAC systems must cope with a wide range of climate extremes. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has noted a significant rise in air conditioning demand, driven by more frequent heatwaves in the southern U.S. and globally. Over the past decade, cooling-related energy consumption has increased by about 10%, with further growth expected as temperatures continue to rise. This surge in demand is a major contributor to overall electricity use in buildings, and without improved efficiency measures, cooling is projected to increase by 50% by 2030.
In contrast, the northern regions, particularly in Canada, experience long, harsh winters that place enormous demand on heating systems. Seasonal temperature extremes, combined with an aging infrastructure, push HVAC systems to their limits, leading to excessive energy consumption.

4. Poor Building Design and Insulation
Inefficient building designs contribute significantly to the high energy consumption of HVAC systems. Many older buildings lack the insulation, energy-efficient windows, and other design features necessary to reduce the workload on HVAC systems. Studies show that buildings with poor insulation can increase HVAC energy usage by as much as 30%.
This inefficiency creates a continuous cycle of energy waste, as HVAC systems must work harder to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, particularly during seasonal extremes.
Causes of High Energy Consumption in HVAC Systems
1. Inefficient Building Designs
Many buildings in North America were constructed long before energy-efficient architectural principles became a priority. Poorly insulated walls, outdated windows, and inadequate building envelopes force HVAC systems to work overtime, increasing energy usage unnecessarily.
According to the EPA, improving building insulation alone could save an average of 15% on heating and cooling costs, demonstrating the outsized impact that small design improvements can have on overall energy use. This is achieved by reducing heat transfer, allowing HVAC systems to operate more efficiently. Insulating key areas such as attics, floors, and walls can significantly reduce the workload on heating and cooling systems, ultimately lowering energy bills and improving comfort.
2. Non-Integrated HVAC Systems
A significant amount of energy is wasted when HVAC systems operate in isolation, without integrating into a building's broader energy management infrastructure. When systems run independently, they cannot make real-time adjustments based on occupancy, outdoor temperature, or energy price fluctuations. This lack of integration leaves buildings operating inefficiently, with energy savings that could be realized through smarter coordination between systems left untapped.
3. Infrequent Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring that HVAC systems run at peak efficiency. However, many systems are neglected, with clogged filters, dirty ducts, or malfunctioning parts leading to energy waste. According to sources such as ENERGY STAR and Mitsubishi Electric, a poorly maintained HVAC system can consume 10-25% more energy than a well-maintained one. This increased energy consumption is primarily due to the system working harder to achieve the same level of temperature control, often caused by factors like clogged filters, unclean coils, or refrigerant leaks. By regularly maintaining your HVAC system, such as cleaning filters and coils, and checking for leaks, you can ensure its efficient operation, ultimately saving energy and reducing costs
Solutions for Reducing HVAC Energy Consumption
1. Smart HVAC Systems
One of the most promising methods of reducing HVAC energy consumption is the integration of smart systems. These systems use sensors, data analytics, and AI to monitor real-time building conditions, adjusting heating, cooling, and ventilation based on actual demand. This approach helps avoid energy waste while maintaining comfort.
Smart thermostats and smart HVAC systems have been shown to reduce energy consumption by as much as 35%, as per the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE). These technologies optimize energy use by adjusting temperature settings based on occupancy patterns and external weather conditions, significantly minimizing air conditioner runtime. Additionally, these systems can learn the daily routines of occupants, allowing for dynamic and efficient temperature control without sacrificing comfort.
2. Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) Systems
Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV) systems are a key innovation in reducing HVAC energy consumption. They work by transferring both heat and moisture between outgoing and incoming air streams, allowing them to recover up to 70-80% of the energy that would otherwise be lost during ventilation. This process reduces the load on HVAC systems, leading to substantial energy savings by preconditioning the fresh air, thus minimizing the need for additional heating or cooling.
3. Low-Pressure Filtration Systems
Low-pressure filtration systems are an often-overlooked solution for improving HVAC efficiency. Traditional air filters can create a pressure drop in HVAC systems, forcing fans and motors to work harder and use more energy. Low-pressure filters, on the other hand, maintain high air quality standards while reducing the energy needed to circulate air throughout a building.
Low-pressure filtration can allow HVAC systems to operate more efficiently, contributing to HVAC energy savings of an average of 15%. This technology not only saves energy but also enhances indoor air quality, making it a win-win solution for energy efficiency and occupant health.
4. Retrofitting and Building Modernization
Retrofitting older buildings with modern, energy-efficient systems offers enormous potential for energy savings. Simple measures, such as installing energy-efficient windows, adding insulation, or upgrading HVAC systems to more efficient models, can significantly reduce energy consumption.
A study by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) indicates that retrofitting older buildings can result in energy savings of 20-30%. One key technology that plays a significant role in these savings is Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems, which offer precise control of heating and cooling across different zones within a building. VRF systems are particularly beneficial for large, multi-zone buildings, where they can achieve energy savings of up to 42% compared to traditional HVAC systems by optimizing the distribution of refrigerant to specific areas based on demand.
5. Routine Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular HVAC maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring system efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Essential tasks like replacing filters, cleaning coils, and checking refrigerant levels can prevent small issues from escalating into major energy drains. Studies show that a well-maintained HVAC system can reduce energy consumption by 10-20% over its lifespan. Additionally, integrating HVAC systems into a building's energy management platform allows for real-time monitoring and adjustments, further optimizing energy use.
The Future of HVAC: A Move Towards Sustainability
The HVAC industry is at a critical juncture, as regulatory pressures and technological innovations are reshaping its future. Governments across North America are tightening energy efficiency standards, with both Canada’s Energy Efficiency Regulations and the U.S. DOE’s energy conservation standards for HVAC systems becoming more stringent. This is pushing the industry toward adopting more sustainable practices.
A major focus for the future of HVAC is the decarbonization of systems, with a shift away from fossil fuel-based heating and cooling. Innovations such as heat pumps, which transfer heat more efficiently and use less energy, are gaining popularity. Heat pumps can reduce energy consumption by up to 50%, making them a highly attractive option for both residential and commercial applications.
In addition to heat pumps, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar-powered HVAC systems, is set to become more widespread. Solar-assisted cooling and heating systems offer the potential to dramatically cut the sector’s reliance on non-renewable energy sources, further reducing its carbon footprint.
The HVAC industry is a major energy consumer, accounting for a significant share of North America's total energy use. Factors such as aging infrastructure, inefficient building designs, and a slow pace of innovation have kept energy consumption high. However, there is hope on the horizon, as emerging technologies and stricter regulations are driving the industry toward a more sustainable future.
By adopting smart systems, low-pressure filtration, and energy-efficient building practices, property owners can reduce HVAC energy consumption, cut costs, and contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable environment. The HVAC industry must embrace innovation and modernization to meet the growing demand for energy-efficient, sustainable solutions—creating a future where indoor comfort and environmental responsibility go hand in hand.
















